What Are Fringe Benefits?
Fringe Benefits: Fringe benefits are additions to compensation that companies give their employees. Some benefits are given universally to all employees of a company while others may be offered only to those at executive levels. Some benefits are awarded to compensate employees for costs related to their work while others are geared to general job satisfaction.
The majority of employers in the private and public sectors offer their employees a variety of benefits in addition to their salaries. These on-the-job perks, typically referred to as fringe benefits, are viewed as compensation by an employer but are generally not included in an employee’s taxable income. A wide range of fringe benefits exist, and what is offered varies from one employer to another.
Read Also: EBITDA formula
The most common benefits include life, disability, and health insurance bundles; tuition reimbursement or education assistance; fitness center access or discounts; employee meals and cafeteria plans; dependent care assistance; and retirement plan contributions.

What Are Fringe Benefits
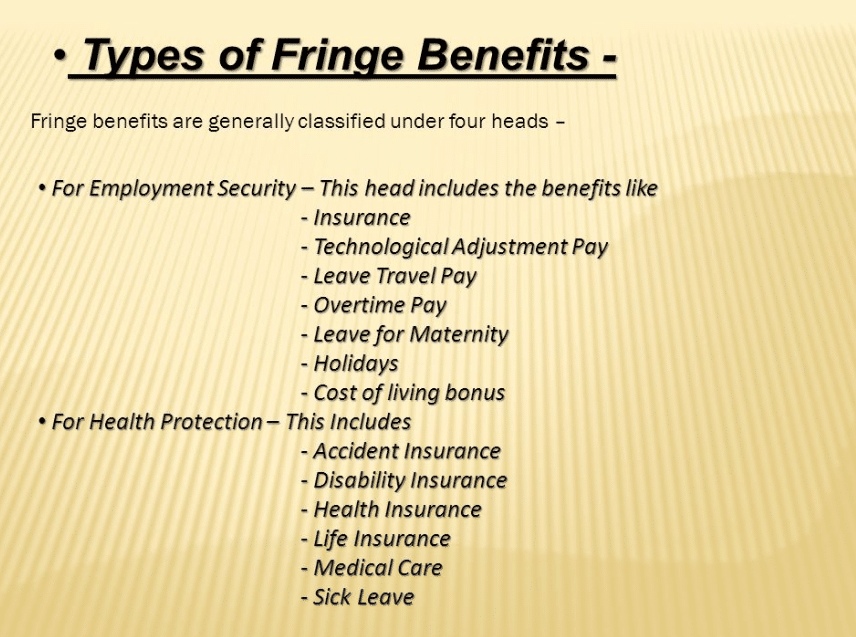
Common fringe benefits include health insurance, life insurance, tuition assistance, childcare reimbursement, cafeteria subsidies, below-market loans, employee discounts, employee stock options, and personal use of a company-owned vehicle.
Uncommon fringe benefits may fit the company profile. PetSmart And Dogtopia both operate pet-friendly workplaces. Ben&Jerry’s rewards its workers with free ice cream. Patagonia’s headquarters features extensive volleyball courts and yoga classes.
The companies that compete for the best talent in highly competitive fields may offer the most extraordinary fringe benefits. Alphabet, the parent company of Google, is known for its benefits that include free commuter bus service and a free gourmet cafeteria. Microsoft gives 20 weeks of paid time off to new birth mothers and 12 weeks for other new parents.
Fringe Benefits Definition
In addition to an employee’s wages, like a company car, health insurance, or life insurance coverage. Any benefit you offer employees in exchange for their services (not including salary) is a fringe benefit.
Offer competitive employee benefits to attract job hunters. One study found that employee benefits were very important to 25.2% of job seekers, moderately important to 31.2%, and somewhat important to 33.8%. Only 9.8% said benefits weren’t important. But, benefits can end up costing you, like if the cost of the benefits rises annually.
There are quite a few different types of fringe benefits to offer employees. Generally speaking, fringe benefits are taxable. But, there are some fringe benefit options that are nontaxable.
Fringe benefits aren’t only for your employees. You can also offer benefits to independent contractors. Independent contractors are workers you hire for a specific job. Unlike your employees, you do not include independent contractors on your payroll or take out taxes. However, you still pay them for the work they do in regular wages and even fringe benefits.
Business partners can also receive benefits. benefits to independent contractors and partners are not taxed. But, you should report the benefit:
- Independent contractor: Use Form 1099-MISC, Miscellaneous Income
Partner: Use Schedule K-1 (Form 1065), Partner’s Share of Income, Deductions, Credits, etc.
As with wages, most benefits are subject to federal income taxes: FICA and FUTA. Unless the IRS explicitly says a fringe benefit is nontaxable, you will need to withhold taxes from fringe benefits in order to correctly deposit and report taxes.
Some taxable benefits include cash bonus pay, paid personal time off, and use of business vehicles (if used outside of business).
You must determine the value of the employee benefits by January 31 of the year after you give them to your employees.
Read Also: Capital One Business Checking
For federal income tax withholding, you can either add the value of the benefits to the employee’s regular wages, or you can withhold at the benefits tax rate of 22% (the same rate for supplemental pay). Withhold FICA tax (Social Security and Medicare taxes) on the benefits added to the employee’s wages.
Since FUTA taxes are paid by the employer and not the employee, you will use the employee’s total compensation to determine your FUTA liability.
What are the examples of fringe benefits?
Common examples of benefits include medical and dental insurance, use of a company car, housing allowance, educational assistance, vacation pay, sick pay, meals, and employee discounts. Total compensation includes regular income and all of these paid benefits.
What are the benefits of fringe benefits?
- Medical and dental insurance.
- Year-end and performance bonuses.
- 401k, IRA, or another employer-sponsored retirement plan, including employee matching contribution plans.
- Employee profit sharing.
- A company car or SUV.
- Housing allowance.
- Educational assistance.
- Vacation and vacation pay.
Are Workers Comp a fringe benefit?
Taxable Fringe Benefit
Definition: Fringe benefits can be defined as any additional compensation provided to an employee that is not directly related to wages. The concept could also be interpreted as any kind of reward granted by an employer to any of its employees aside from their wages.
De Minimis Fringe Benefit
benefits are a commonly used tool to reward employees for their performance or to lift up the work conditions of the company. There are many different types of benefits, but the purpose of them is normally to motivate, compensate, and provide a more comfortable work or personal situation to the beneficiary.
Companies often offer benefits like auto insurance, medical insurance, employer-provided cell phones, expense reimbursements, educational assistance, employee discounts, and many others. For employees, a fringe benefit is a great way to save more money since the company takes on some of their regular expenses, like in the case of insurance policies or cell phones. In some instances, these benefits are tax-exempt, like in the case of health insurance.
Fringe Benefits Examples
The following list of fringe benefits is subject to exclusion rules:
- Accident and health benefits
- Achievement awards
- Adoption assistance (only exempt from federal income tax)
- Athletic facilities
- De minimis (minimal) benefits
- Dependent care assistance
- Educational assistance program
- Employee discounts
- Employee stock options
- Employer-provided cell phones
- Group-term life insurance coverage
- Health savings accounts (HSAs)
- Lodging on business premises
- Meals
- Moving expense reimbursements
- No-additional-cost services
- Retirement planning services
- Transportation (commuting) benefits
- Tuition reduction
- Working condition benefits
Be aware that some fringe benefits are only nontaxable in certain situations. Some taxes could apply. For example, group-term life insurance coverage is only exempt from FICA tax up to the cost of $50,000.
